You might know that Arlington was once a part of Washington D.C., but did you know that Arlington’s boundary stones are some of the country’s oldest federal monuments?
These stones were created as a result of the Residence Act of 1790, which gave President George Washington permission to select an area for a new Federal capital along the Potomac River.
To facilitate this deal, both Maryland and Virginia agreed to cede a section of land, with Virginia ceding much of what is now Arlington. Since 1731, the Virginia land had been designated as part of Fairfax County.
Washington selected the southernmost section of the Potomac River in order to include as much of Virginia and the city of Alexandria as possible. Although Arlington was largely rural at the time, Alexandria was one of the most important port cities in the region.
The Survey
Once the boundaries had been chosen, then Secretary of State Thomas Jefferson appointed Major Andrew Ellicott to survey the 10 square mile area for an official border. Ellicott was chosen because he was one of the most prominent surveyors of the time and possessed some of the most advanced mapping equipment of the time period. He was joined by Benjamin Banneker, a free black man who had taught himself mathematics and astronomy.
The men set up camp at Jones Point, Alexandria and worked with a small team to chart the stars and complete the necessary calculations for drawing the borders.
Arlington at the time was mostly rural with dense forests, making surveying work extremely dangerous for the men in the field. Many suffered from the harsh climate, influenza, and one worker was even killed by a falling tree.
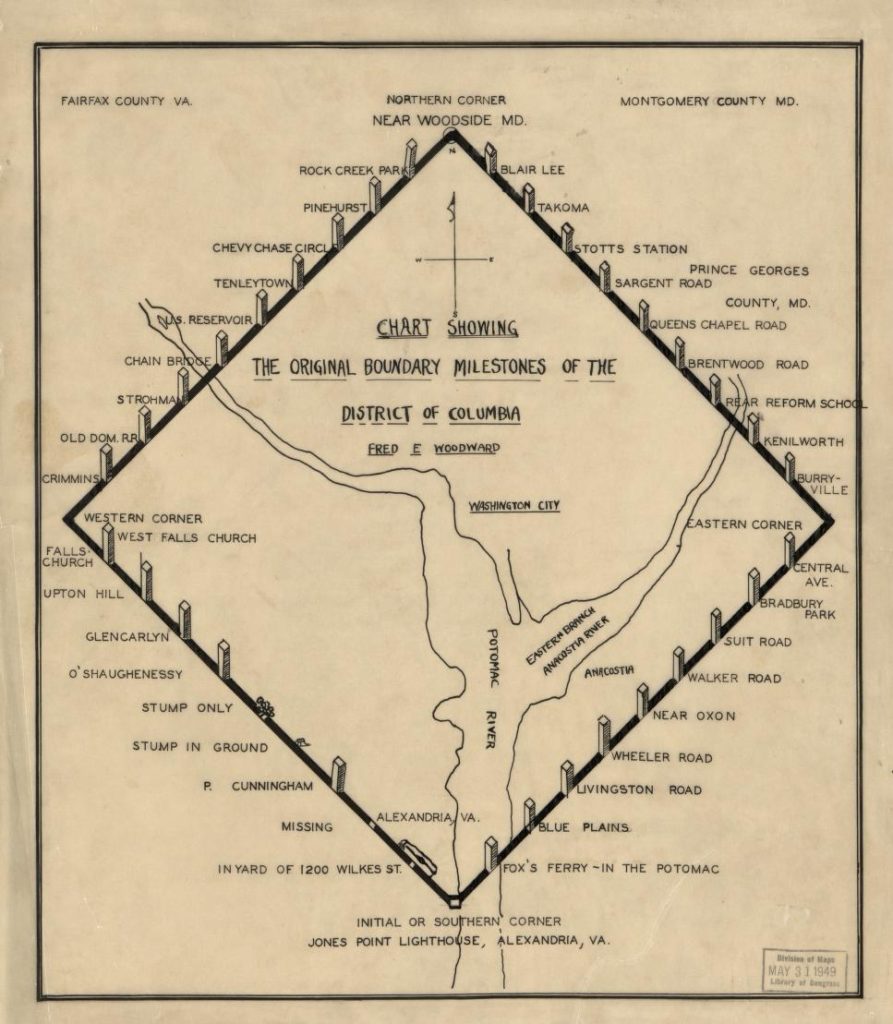
Chart showing the original boundary milestones of the District of Columbia / Fred E. Woodward (1906).
Image Courtesy of the Library of Congress
The First Stone
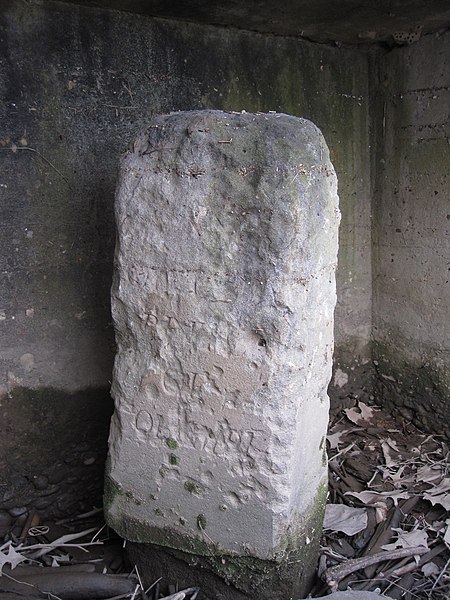
The first boundary stone was set up at Jones Point on April 15th, 1791. Ellicott and his team (now without Banneker, who had retired due to his health shortly after the first marker was placed), then began the process of placing the remaining 39 boundary stones across Virginia and Maryland.
Each stone was made of sandstone from Aquia Creek and placed at one-mile intervals. Engraved on each marker was “Jurisdiction of the United States”, with the accompanying state and year the stone was placed.
By the end of 1791, 14 stones had been placed in Virginia and the remaining 26 were erected in Maryland the following year. It would take another 10 years for the District of Columbia to be formally incorporated, with the federal capital remaining in Philadelphia until 1801.
The First Boundary Stone under Jones Point Lighthouse, Alexandria in 2010; Image Courtesy of Something Original at Wikipedia
Preservation Today
The stones would remain in place while the face of the city changed around them, often leading to some stones being buried or lost in the growth of nature. The section of Virginia that is now Arlington and Alexandria would remain as part of D.C. until 1847, when unhappy Virginia citizens forced the federal government to give the land back to the Commonwealth.
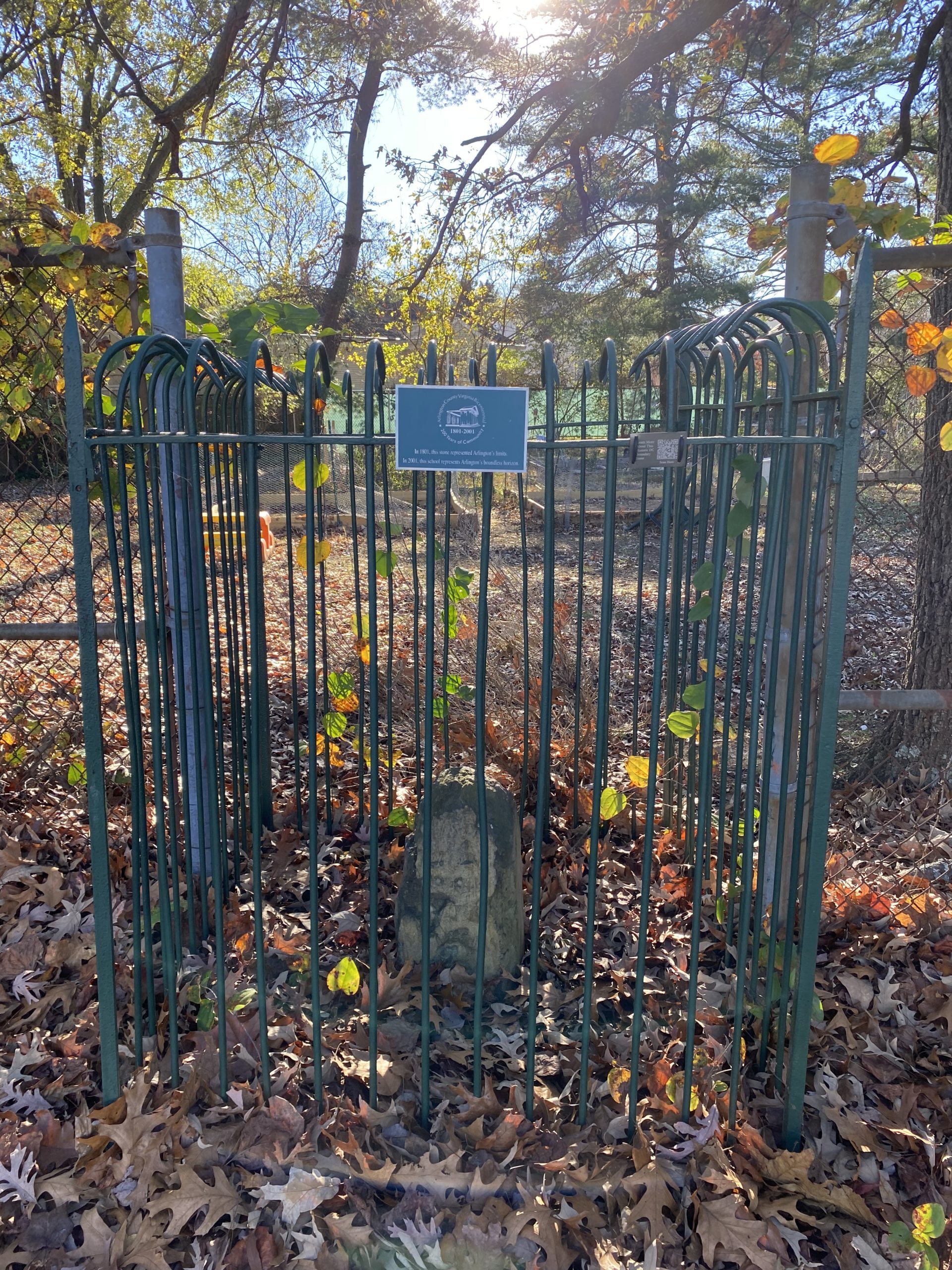
Boundary stone preservation efforts began in 1915, as the Daughters of the American Revolution (DAR) began placing iron cages around the remaining markers. Although some of the remaining monuments today lie on private property, there are 36 stones that can be visited across the D.C. area.
To explore the Boundary Stones online, visit the Boundary Stones of DC Story Map
Boundary Stone No. 9 SW at Benjamin Banneker Park, Arlington, photo 2022, CLH.
Do you have a question about this story, or a personal experience to share?
Use this form to send a message to the Center for Local History.
Center For Local History - Blog Post Message Form
Do you have a question about this story, or a personal experience to share? Use this form to send a message to the Center for Local History.
"*" indicates required fields